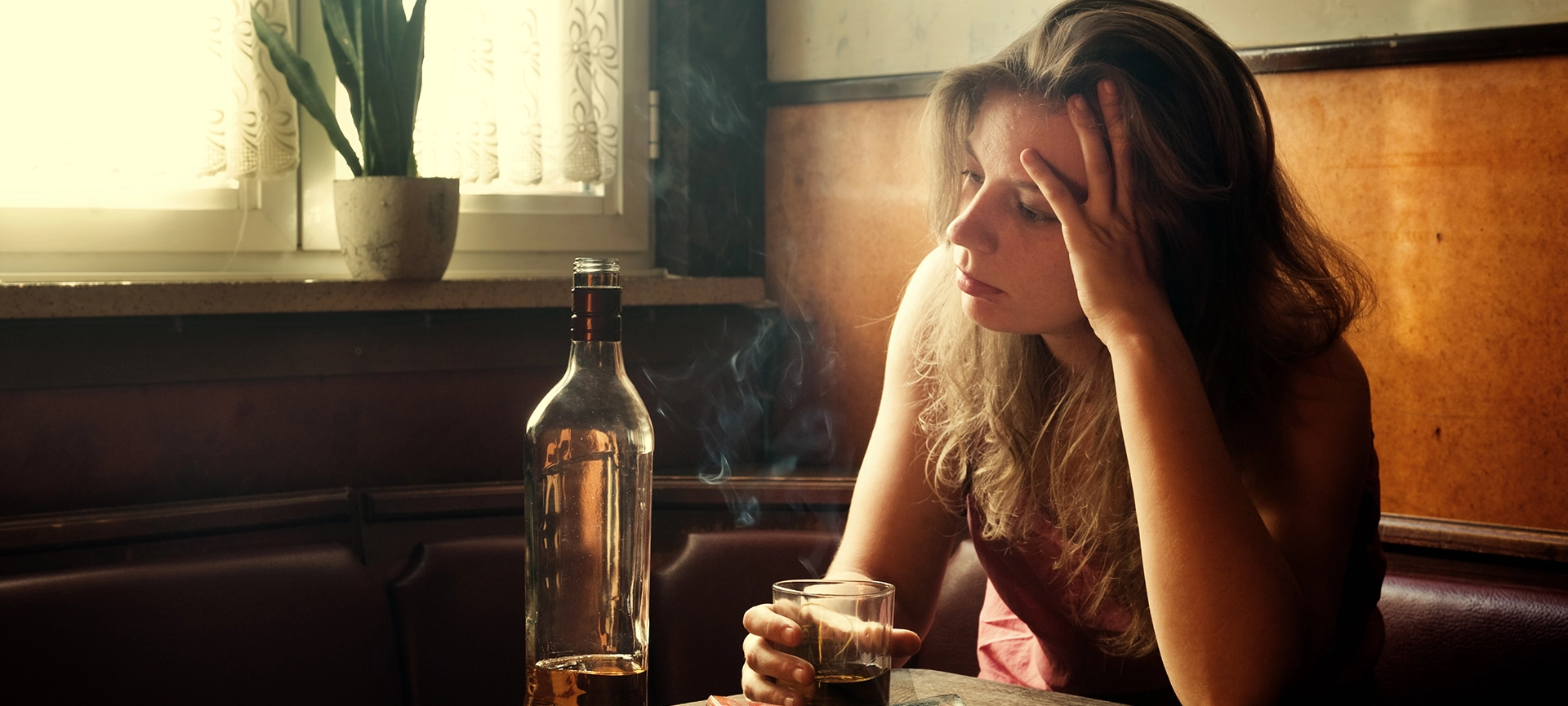
Drinking is a common social activity that many individuals enjoy. However alcohol is addictive, and with time, social drinking can become alcohol abuse and dependence. At this point, drinking will start to cause negative physical and emotional effects and memory loss.
Excessive drinking can wreak havoc on the body, including the memory. Memory is an essential cognitive function that stores, processes and retrieves information.
Here, we’ll explore how continued alcohol abuse can impact your memory. We’ll also explore solutions to reverse the effects of drinking on your memory.
How Alcohol Affects Memory
Alcohol can affect memory in various ways. Some of the ways include:
Disrupts Brain Function
Alcohol disrupts brain function, leading to impaired memory formation and consolidation. It affects the hippocampus, which is the area of the brain responsible for memory formation and consolidation.
Alcohol abuse can have profound effects on brain function. Alcohol is a depressant that slows down the central nervous system, including the brain. Prolonged alcohol use can lead to changes in the brain’s function, affecting various areas, including the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum.
The prefrontal cortex is responsible for decision-making, impulse control, and judgment. Alcohol abuse can damage this area, leading to impulsive behaviour and poor decision-making. The hippocampus is essential for memory formation and learning. Alcohol can impair the hippocampus, leading to memory loss and difficulty learning new information.
The cerebellum is involved in movement coordination and balance. Alcohol abuse can cause damage to this area, leading to motor impairment and coordination problems.
Interferes with REM Sleep
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep is essential for memory consolidation. Drinking can interfere with REM sleep, leading to fragmented sleep and impaired memory consolidation.
The REM stage is responsible for consolidating memories and facilitating learning. Studies have shown that alcohol consumption can disrupt the REM stage, leading to a decreased ability to form new memories and consolidate existing ones.
Alcohol consumption can also lead to fragmented sleep, which can further impair memory consolidation. Alcohol can reduce the time spent in REM sleep, decreasing the amount of time available for the brain to consolidate memories. Additionally, alcohol can affect the ability to enter deeper sleep stages, further affecting memory consolidation.
Furthermore, alcohol can interfere with the brain’s ability to form new neural connections, which is essential for learning and memory formation. As a result, chronic alcohol use can lead to cognitive deficits, including memory problems.
Affects Brain Structure
Chronic alcohol use can affect brain structure, leading to brain shrinkage and reduced brain volume. This can affect memory and cognitive function.
Chronic alcohol use can cause structural changes in the brain, including brain shrinkage and damage to white matter.
Alcohol consumption can damage the hippocampus, a region of the brain involved in memory formation and learning. Prolonged alcohol use can reduce the hippocampus’s size, impairing the ability to form new memories.
Additionally, alcohol can damage the prefrontal cortex, a region responsible for decision-making, impulse control, and judgment, which can further affect memory consolidation.
Alcohol can also interfere with the brain’s ability to form new neural connections, which is essential for learning and memory formation. The damage caused by alcohol abuse can be irreversible, leading to long-term cognitive deficits, including memory problems.
Related Article: The Signs That My Loved One Needs Help With Drug And Alcohol Abuse In Toronto, Ontario

Types of Memory Affected by Drinking
Drinking can affect different types of memory, including:
Working Memory
Working memory is responsible for holding and manipulating information in the short term. Drinking can impair working memory, leading to difficulties in completing tasks that require concentration and attention.
Long-term Memory
Long-term memory is responsible for storing information for an extended period. Drinking can impair long-term memory formation and consolidation, leading to difficulty retrieving information.
Episodic Memory
Episodic memory is responsible for storing and retrieving specific events or experiences. Drinking can impair episodic memory, leading to difficulty in remembering events and experiences.
Factors that Affect the Impact of Drinking on Memory
The impact of drinking on memory varies depending on various factors, including:
- Age: The older an individual gets, the more vulnerable they become to the effects of drinking on memory.
- Gender: Women are more vulnerable to the effects of drinking on memory than men.
- Amount of Alcohol Consumed: The more alcohol an individual consumes, the more significant the impact on memory.
- Frequency of Drinking: Regular heavy drinking can have a more significant impact on memory than occasional heavy drinking.
- Drinking Patterns: Drinking patterns, such as binge drinking, can have a more significant impact on memory than moderate drinking.
Ways to Improve Memory Impacted by Drinking
Fortunately, there are ways to improve memory that have been impacted by drinking. Some of these ways include:
Reduce Alcohol Consumption
The most effective way to improve memory impacted by drinking is to reduce alcohol consumption. This can help to prevent further damage to the brain and allow it to recover.
This is possible when you sign up for an alcohol addiction program. Together with the support of experienced specialists, you can stop drinking while managing any associated withdrawal symptoms.
Exercise
Exercise has been shown to improve memory and cognitive function. It can also help to reduce the negative effects of drinking on memory.
Healthy Diet
A healthy diet can help to improve memory and cognitive function. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help to support brain health and improve memory.
Get Adequate Sleep
Adequate sleep is essential for memory consolidation. Getting enough sleep can help to improve memory and cognitive function.
Cognitive Training
Cognitive training, such as brain games, can help to improve memory and cognitive function. These activities can help to stimulate the brain and improve memory.
Related Article: Types of Alcohol Rehab Programs: Which Treatment Option is Right for You?

In the End
Drinking can affect your memory in many different ways. Alcohol abuse affects your brain’s normal function. It also changes your brain structure, impeding its normal ability to form and hold new memories.
If you or a loved one is abusing alcohol, it’s better to take pre-emptive steps to beat the addiction before the damaging effects on your memory become prominent. Here at Addiction Rehab Toronto, we offer varied alcohol treatment programs to help you achieve long-term sobriety.
Call us via +1 855-787-2424 to learn more about our alcohol addiction treatment programs.